What is titanium dioxide used for? Should it be avoided?
Release time: May 1, 2025
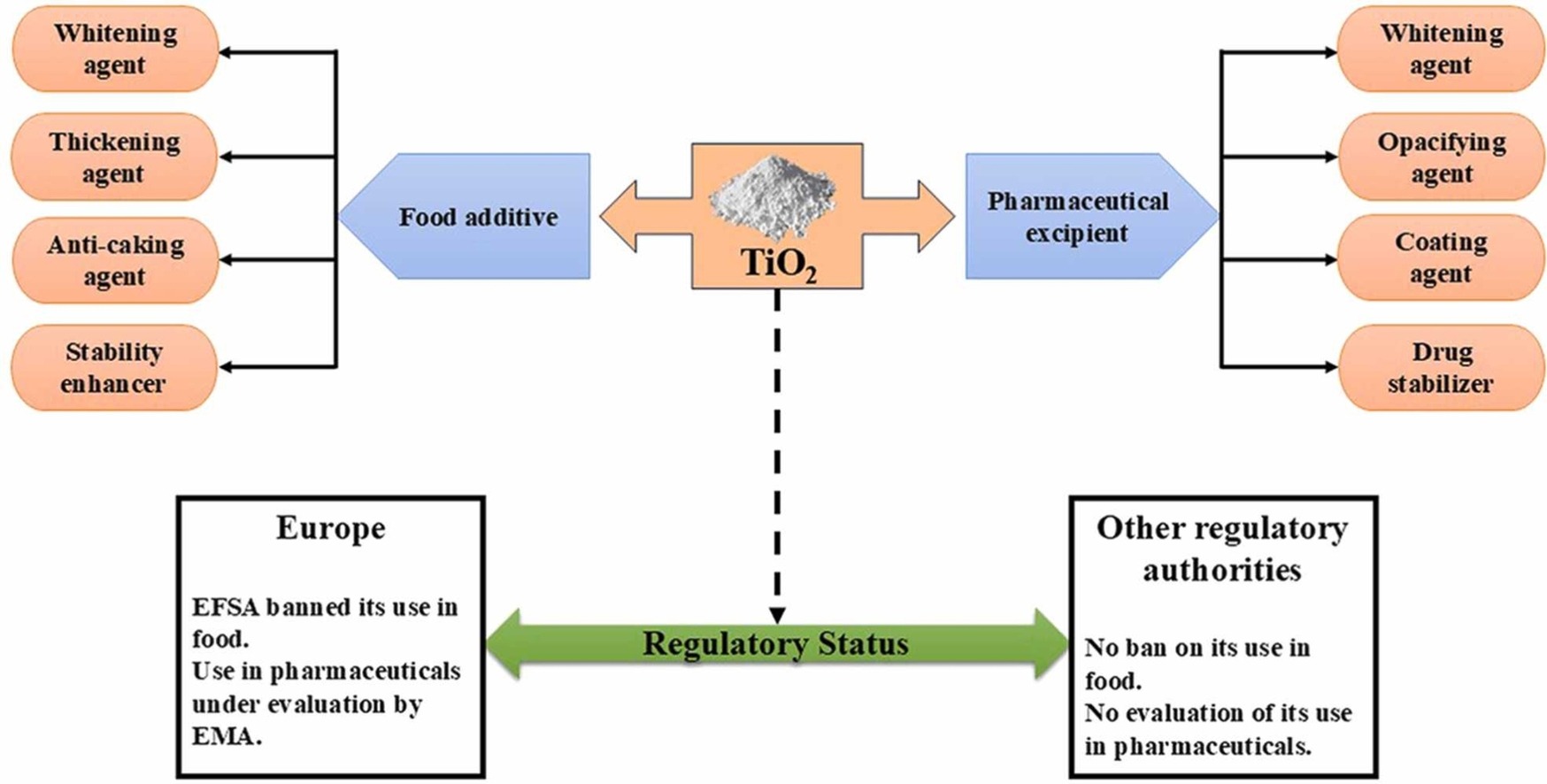
Titanium dioxide (TiO₂, CAS No. 13463-67-7) is a white, powdery substance found everywhere—from your sunscreen to your toothpaste, and even in some foods. But is it safe? Let’s break down its uses and the controversies surrounding it.
Why Is Titanium Dioxide Everywhere?
Thanks to its brightness, opacity, and ability to block UV rays, titanium dioxide is a superstar in many industries:
-
Cosmetics & Sunscreens
-
Acts as a physical UV filter in sunscreens, reflecting harmful UVA/UVB rays.
-
Adds whiteness and thickness to foundations, powders, and toothpaste.
-
-
Food (Labeled as E171 in the EU)
-
Used to brighten candies, chewing gum, icing, and dairy products.
-
But take note: The EU banned E171 in 2022 over safety concerns, while other countries (like the U.S. and Canada) still allow it.
-
-
Paints, Plastics, and Paper
-
The go-to white pigment for coatings, plastics, and paper due to its durability and shine.
-
-
Medicines
-
Coats pills and capsules to make them look clean and professional.
-
Should You Avoid It? The Safety Debate
The answer isn’t black or white—it depends on how you’re exposed to it.
✅ Generally Safe
-
Topical use (sunscreens, makeup): No significant risk when applied to skin.
-
Non-nano forms in paints/plastics: Harmless unless inhaled as dust.
⚠️ Proceed with Caution
-
Inhalation risk: Industrial workers handling TiO₂ powder face higher exposure. The IARC classifies inhaled TiO₂ dust as a possible carcinogen (Group 2B).
-
Food (E171): The EU banned it due to concerns about nanoparticle accumulation and potential DNA damage, though human evidence remains limited.
❌ When to Avoid
-
Spray sunscreens: Nano-particles could be inhaled; opt for lotions instead.
-
Processed foods in the EU: Choose E171-free products if you’re cautious.
The Bottom Line
| Use Case | Safety Level | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Sunscreens/makeup | Safe | Stick to lotions, avoid sprays |
| Paints/plastics | Safe | Don’t inhale dust |
| Food (E171) | Controversial | Limit intake, especially for kids |
| Industrial dust | Risky | Wear protective gear |
Final Tip: If you’re wary, check labels for "nano-TiO₂" in cosmetics or "E171" in foods. For most people, everyday use poses little risk—but staying informed never hurts!
Science evolves, and so do regulations. What’s deemed safe today might be re-evaluated tomorrow. When in doubt, moderation is key.
Can I get tirzepatide for weight loss? What are the drawbacks of tirzepatide?
If you’ve been following the latest buzz in weight loss medications, you’ve probably heard of tirzepatide (brand names: Mounjaro for diabetes, Zepbound for weight loss). This once-weekly injection has been hailed as a game-changer for obesity treatment—but how does it work, who can use it, and what are the downsides? Let’s break it down.
What is 2-ethylhexyl acrylate used for? Is 2-ethylhexyl acrylate toxic?
Have you ever wondered what makes certain adhesives stick so well or why some paints remain flexible and durable? The answer might lie in a chemical called 2-ethylhexyl acrylate (2-EHA, CAS No. 103-11-7). This colorless, fruity-smelling liquid is a key ingredient in many everyday products, from adhesives and coatings to textiles and personal care items.
Sulfuric Acid
CAS number:7664-93-9
Diacetone Alcohol
CAS number:123-42-2
Potassium chloride
CAS number:7447-40-7
Contact Us
We supply all kinds of reagents and raw materials, focus on research and development, and integrate chemical synthesis, purification technology and small-scale, pilot and mass production supply chain construction.Email:net.fei@163.com
