What is isophorone used for? Is isophorone toxic?
Release time: May 5, 2025
If you’ve ever wondered about the chemicals behind everyday products—from vibrant paints to life-saving medical imaging—isophorone might surprise you. This versatile organic compound, with its camphor-like smell, plays a hidden but critical role in industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare. But what exactly is it, and should we be concerned about its safety? Let’s break it down.
What Is Isophorone?
Isophorone (CAS No 78-59-1, chemical formula: C₉H₁₄O) is a colorless or pale yellow liquid derived from acetone. Its unique structure makes it a valuable building block in chemistry, serving as a solvent, a precursor for high-performance materials, and even a component in cutting-edge medical technologies.
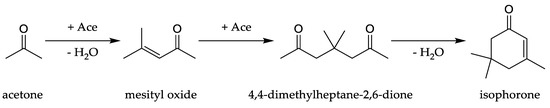
What Is Isophorone Used For?
-
Industrial Solvent
Isophorone is a star in coatings, inks, and adhesives due to its excellent ability to dissolve other substances while evaporating cleanly. Imagine the glossy finish on your car or the durability of industrial paints—isophorone often helps achieve these properties. -
Chemical Middleman
It’s transformed into isophorone diamine (IPDA) and isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI), key ingredients in polyurethane foams (think insulation, mattresses) and epoxy resins (used in aerospace and electronics).
-
Medical and Environmental Tech
-
Fluorescent Probes: Recent studies (e.g., Sensors and Actuators B, 2024) highlight isophorone-based probes that detect cancer biomarkers or monitor pH levels in real time. These tools help surgeons identify tumors or track environmental pollutants.
-
Biofuels: Scientists are converting isophorone into high-energy biofuels for jets, boasting higher efficiency and lower emissions (Fuel, 2025).
-
-
Fragrances and Pesticides
Its subtle camphor scent lends itself to perfumes, while its derivatives act as intermediates in agrochemicals.
Is Isophorone Toxic?
Like many chemicals, the answer depends on exposure:
-
Safety Concerns:
-
Flammable: Keep it away from open flames.
-
Irritant: Direct contact can irritate eyes, skin, or lungs. Proper protective gear (gloves, masks) is essential in industrial settings.
-
Environmental Impact: Waste must be managed carefully to avoid ecosystem harm.
-
-
Low-Risk in Controlled Use:
-
In finished products (e.g., cured paints or plastics), isophorone is typically locked into stable forms, minimizing exposure.
-
Regulatory agencies approve its use in cosmetics and medicines at safe concentrations, citing decades of research (International Journal of Toxicology, 2024).
-
Key Takeaway: While raw isophorone requires caution, its applications are designed to mitigate risks—much like how alcohol is toxic in pure form but safe in hand sanitizers.
The Future of Isophorone
Innovations are expanding its roles:
-
Green Chemistry: Researchers are optimizing production to reduce waste (e.g., domino annulation reactions, Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2025).
-
Smart Materials: From foldable screens to self-healing coatings, isophorone-derived polymers are pushing boundaries.
Summary
Isophorone is a multitasking molecule that fuels modern technology—from your smartphone’s epoxy casing to cancer diagnostics. While handling it raw demands care, its engineered uses are tightly regulated for safety. As science advances, isophorone’s potential keeps growing, proving that even obscure chemicals can be unsung heroes of innovation.
Next time you see a glossy paint job or hear about a medical breakthrough, remember: isophorone might be working behind the scenes!
References:
-
Sensors and Actuators B (2024) on fluorescent probes.
-
Fuel (2025) on biofuel applications.
-
International Journal of Toxicology (2024) on cosmetic safety.
Is xanthine a bronchodilator? What foods contain xanthine?
Have you ever wondered why your morning coffee perks you up or how chocolate can feel so energizing? The answer lies in a tiny molecule called xanthine, CAS No. 69-89-6. Found in everything from tea leaves to your own body, xanthine is a fascinating compound with roles in metabolism, medicine, and even food freshness. But is it a bronchodilator? And which foods contain it?
Can I get tirzepatide for weight loss? What are the drawbacks of tirzepatide?
If you’ve been following the latest buzz in weight loss medications, you’ve probably heard of tirzepatide (brand names: Mounjaro for diabetes, Zepbound for weight loss). This once-weekly injection has been hailed as a game-changer for obesity treatment—but how does it work, who can use it, and what are the downsides? Let’s break it down.
Bpc 157
CAS number:137525-51-0
Ergothioneine
CAS number:497-30-3
Potassium chloride
CAS number:7447-40-7
Isophorone
CAS number:78-59-1
TITANIUM DIOXIDE (TIO2)
CAS number:13463-67-7
Formaldehyde
CAS number:50-00-0
Contact Us
We supply all kinds of reagents and raw materials, focus on research and development, and integrate chemical synthesis, purification technology and small-scale, pilot and mass production supply chain construction.Email:net.fei@163.com
